Many people have a hard time understanding why cryptocurrencies have value. They think that if they are not backed by a government or something tangible, they cannot be valuable.
Cryptocurrencies have value because users have confidence in them. It is similar with fiat money and gold. If no one believed they had value, they would be worthless. But why do some people have faith in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies? Besides having a network that has been running smoothly since 2009, Bitcoin has something that sets it apart from fiat money: it is scarce. There will never be more than 21 million bitcoins.
In contrast, central banks print the money they want in order to manage the economy from above. As more and more money becomes available, it becomes less and less valuable.
That is why, measured in euros or dollars, Bitcoin is becoming more and more valuable. This digital scarcity was created in the Bitcoin protocol to maintain the value of the currency. While it is possible to create another blockchain similar to Bitcoin (as Bitcoin is free software) and thus create more coins, not everyone would adopt the clone currency, as the value lies mainly in the community of users and the trust acquired over the years. There are a multitude of different currencies that try to compete with Bitcoin, but they only have value because they provide some different functionality and have a community behind them.
How can something digital be scarce?
Unlike other digital assets that can be copied and pasted without limit, cryptocurrencies operate in a decentralized manner with a consensus mechanism that guarantees their security and scarcity. This consensus mechanism varies from cryptocurrency to cryptocurrency. The first consensus mechanism used is based on a process known as proof-of-work, in which computers called miners compete to solve mathematical problems to validate transactions.
Since miners receive financial rewards for mining, there is a large network of computers that keep the network decentralized and running 24 hours a day, every day of the week. Proof of work makes it nearly impossible to reverse or modify a transaction once it is part of the blockchain. Since the network is validated by a large number of actors who receive rewards for their contribution and thus have a stake in the proper functioning of the network, it is not economically feasible to amass more than 50% of the network to maliciously alter the blockchain.
Less and less is being issued
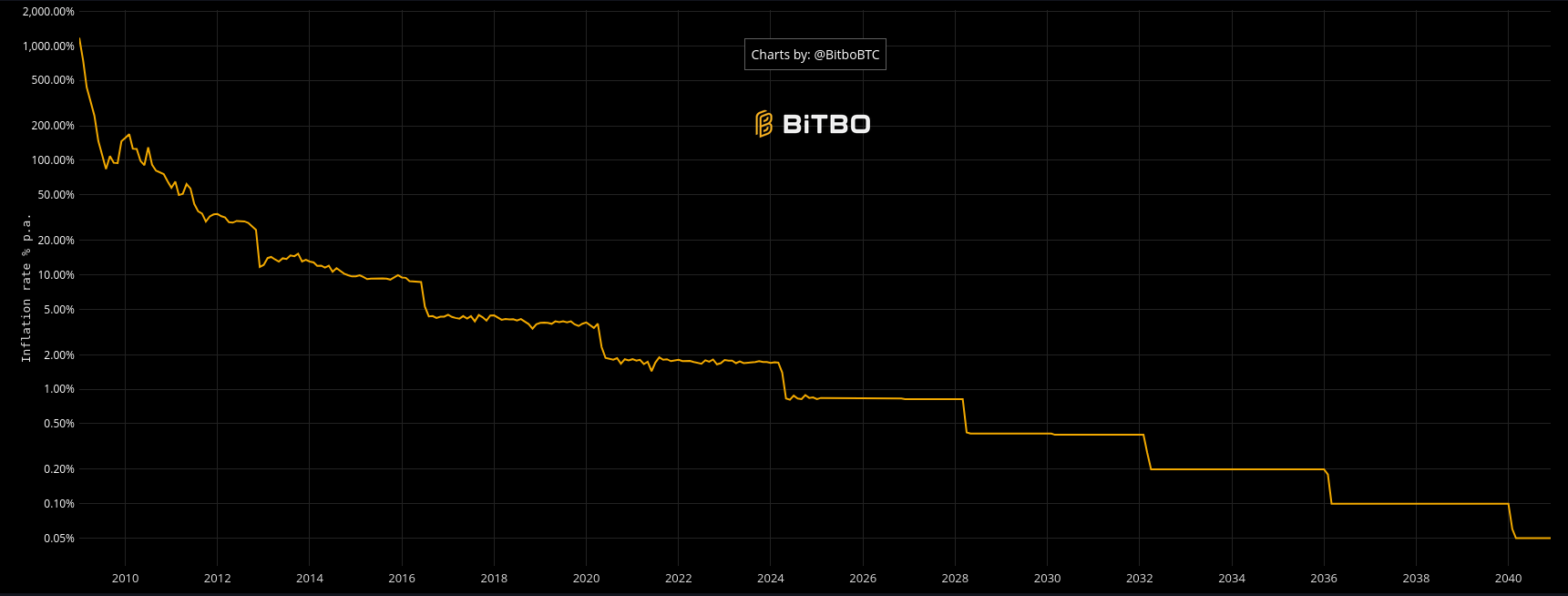
Every four years, Bitcoin reduces the rewards received by miners by half, so fewer and fewer coins are issued. In the year 2140, Bitcoin inflation will be 0%, that means that no new coins will be issued. Miners will then continue to receive rewards because there are fees they receive for validating transactions. Bitcoin's inflation is currently lower than that of gold, making it one of the most coveted assets and one of the fastest growing in value.
No central entity can control or confiscate your bitcoins
Another appeal that makes Bitcoin valuable is that it cannot be confiscated by bankers or anyone else. Nor can payments be reversed, as in the traditional banking system. If you keep your private key secure, no one can take your wealth.
It enables international trade
Thanks to blockchain technology, it is possible to trade with anyone in the world who has access to the Internet. Cryptocurrencies have gained recognition and users across the globe, increasing their value.
Conclusion
As long as the Internet and people who value and believe in this technology continue to exist, Bitcoin and similar cryptocurrencies will continue to increase in value over the long term, as they are deflationary. People who hoard fiat money, on the other hand, will lose purchasing power over time if central banks continue to issue more money.


Comments